In the silent dark, a new age of vision emerges. It’s not the stuff of superhero tales, but of drones that pierce the night. Enhanced by night vision capabilities, these flying marvels navigate the unseen, transforming industries from agriculture to search and rescue.
Equipped with sophisticated thermal imaging and cameras honed for minimal light, these drones redefine what’s possible after sunset. Ever wondered how a drone can detect faint heat signatures or measure distances with laser precision? It’s all in the advanced tech.
In the next sections, we’ll peel back the layers on this remarkable technology. How do these drones work? Why are they indispensable for certain industries? By the end, “seeing in the dark” won’t just be a phrase—it’ll be a reality. Dive in and let’s illuminate the unseen.
Article Highlights
- Night vision drones combine infrared illumination, thermal imaging, and laser rangefinding to revolutionize low-light operations.
- Dual sensors in drones merge night vision and thermal capabilities, maximizing their efficiency across diverse industries.
- From agriculture to search and rescue, thermal drones are redefining tasks by offering unparalleled insights even in challenging conditions.
The Science Behind Night Vision Technology
At its core, night vision is about harnessing light—mostly the kind our eyes can’t detect. Two predominant methods dominate this scene: infrared illumination and thermal imaging. But how do they differ?
The integration of night vision and thermal imaging is revolutionizing operations across industries.
Infrared Illumination: Think of this as a flashlight only your camera can see. Devices with infrared (IR) send out a light invisible to our eyes. When this light bounces off objects and returns, the device captures it, crafting a visible image. It’s a bit like shining a torch in a dark room, only this beam remains hidden to the naked eye.
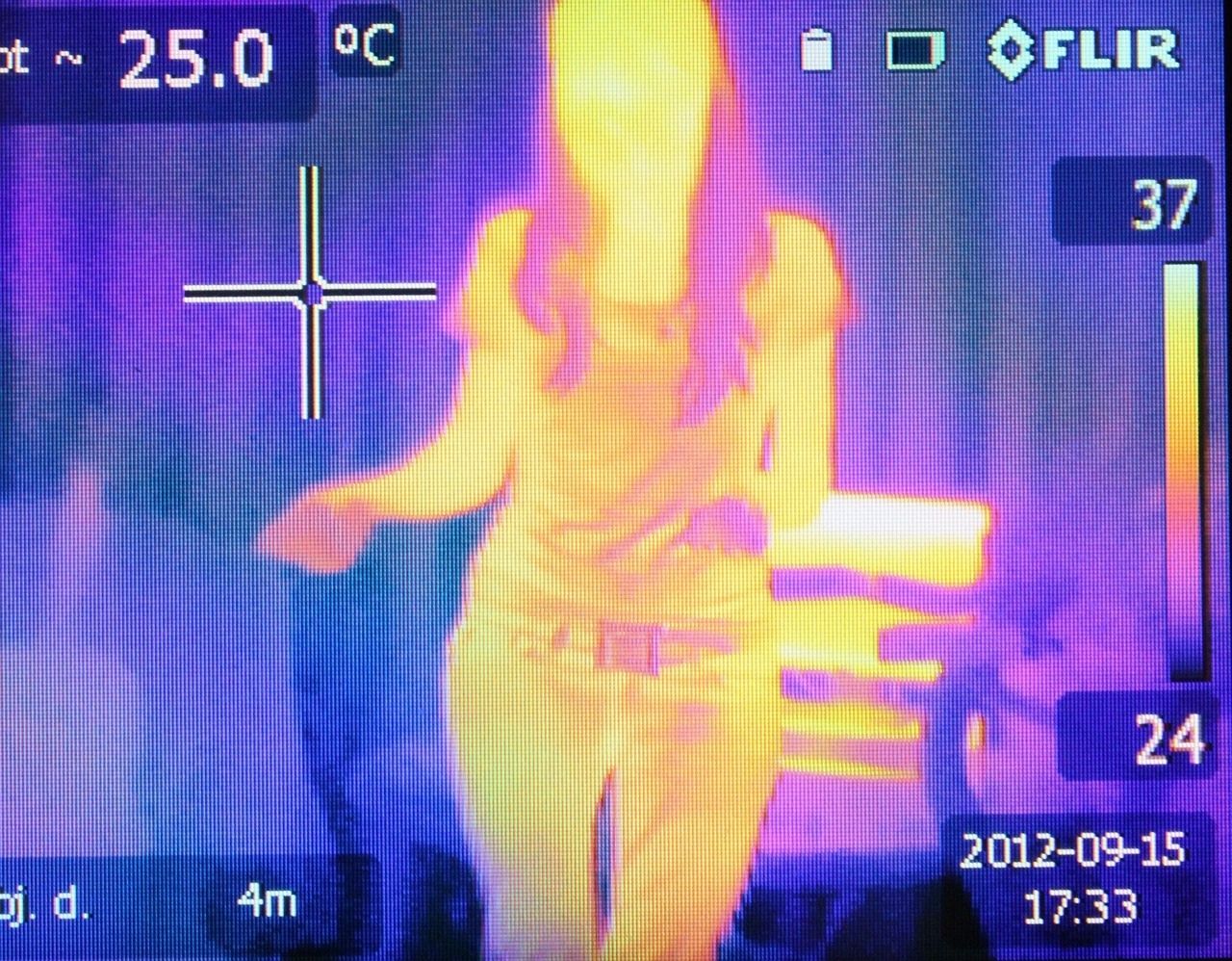
Thermal Imaging: This is less about light and more about heat. Everything, from humans to inanimate objects, emits some form of heat. Thermal cameras detect these heat patterns, then translate them into an image. Instead of relying on light, they focus on temperature differences. So, even in pitch-black conditions, if it’s warm, it’s visible.
In essence, while infrared seeks out its own light reflections, thermal imaging rides on the natural heat waves emitted by objects. Both are revolutionary, but they cater to different needs and scenarios in the vast landscape of drone operations.
What Makes a Night Vision Drone Unique?
In the vast expanse of the drone industry, night vision-equipped drones have emerged as true pioneers. But why is there such a buzz around them?
Infrared and Thermal Cameras: These aren’t your everyday camera systems. They are the eyes that grant drones the power to navigate the unseen. Infrared cameras allow drones to function in absolute darkness by emitting and detecting their own light.
On the other hand, thermal cameras interpret temperature variations, translating this heat data into decipherable images, vital for many professional tasks.
Advantage in Low-Light Operations: While conventional drones can struggle post-sunset, their night vision counterparts don’t skip a beat. Be it the enchanting twilight or a moonless night, these drones ensure uninterrupted operations.
Their prowess isn’t confined to merely ‘seeing’ in dim conditions. It’s about the promise of unwavering precision and efficiency, irrespective of the light conditions.
In essence, night vision drones aren’t just another addition to the drone family. They redefine boundaries, carving out a niche that combines technology with the promise of limitless possibilities.
Dive Deep: Understanding Thermal Imaging
Thermal imaging is like granting the gift of sight to the otherwise invisible. But how exactly does this transformative technology work?
Every object emits some level of infrared radiation, which is directly proportional to its temperature. These infrared emissions are invisible to the human eye, but thermal cameras are uniquely designed to detect them.
The camera captures this radiation, processes it, and translates it into an image called a thermogram. Subsequently, specialized software converts the thermogram into a display where varying temperatures are represented by different colors—typically, hotter objects are depicted in warmer shades, while cooler ones get colder colors.
Imagine a lost hiker in a dense forest or a faulty hot-spot in an extensive solar panel array. In scenarios like these, the detection of minute temperature variations or heat signatures becomes paramount.
By identifying these heat differentials, thermal imaging aids in search and rescue missions, infrastructure maintenance, and even wildlife monitoring.
On the other hand, standard cameras capture visible light to reproduce images. While they excel in well-lit conditions, their utility diminishes under low light or obscured settings.
Thermal cameras, however, aren’t reliant on light at all. Instead, they capture temperature data, offering clarity even in complete darkness or through obstructions like smoke. This distinct advantage allows them to operate effectively in a broader range of scenarios.
Thermal imaging is more than just another camera technology. It’s a game-changer, revealing nuances the naked eye would miss, expanding horizons beyond the limitations of visible light.
The Intricacies of Night Vision Cameras
Infrared night vision cameras are like gateways to a world often unseen. Their ability to function in minimal lighting conditions gives them a significant edge over regular cameras. But what makes them so unique?
Diving into the specifics of a low light camera, one quickly realizes that their mechanism is tailored to amplify available light. These cameras use advanced sensors that are sensitive to infrared light, which is invisible to the human eye.
Once they capture this infrared light, they convert it into an electronic signal, which is then processed and rendered into a viewable image.
In contrast, regular cameras operate primarily within the visible spectrum. They require a fair amount of light to produce clear images. In conditions where light is scarce, these cameras often struggle, resulting in grainy or darkened photos.
Night vision cameras, however, are designed to thrive in such conditions. Their internal processes, such as the use of intensifier tubes in some models, magnify the scant available light, enabling them to produce crisp images even in near-total darkness.
In essence, while regular cameras provide an eye into the well-lit world, night vision cameras unlock the mysteries of the shadows, unveiling details that might otherwise remain hidden.
Thermal and Visual Sensors: The Dual Power
In the realm of drone technology, one innovation stands out for its profound utility: the combination of both night vision and thermal imaging in a single drone. Drones equipped with dual sensors are game-changers, merging the strength of two powerful vision technologies.
Let’s think of it as a superhero team-up. While night vision cameras offer clarity in low light conditions by amplifying available light, thermal imaging cameras detect variations in temperature, turning them into visible images.
The blend of these two ensures that, regardless of the environmental conditions, the drone gets an encompassing view of its surroundings.
One might wonder about the need for such dual capabilities. For industries like search and rescue or wildlife monitoring, it’s invaluable.
In scenarios where a person might be lost in a forest at night, the night vision will provide clear imagery of the terrain, while the thermal imaging can pinpoint the heat signature of the person, facilitating a swift rescue.
Similarly, for professionals conducting infrastructure inspections or monitoring agriculture, having both sensors can be advantageous.
By day, standard visuals can capture detailed imagery; by night or in overcast conditions, the thermal imaging can highlight problem areas or variations in crop health by detecting temperature differences.
Furthermore, the amalgamation of these two technologies saves time. Instead of deploying two separate drones or conducting two different flights, one for thermal imaging and another for night vision, a drone equipped with dual sensors can do both simultaneously.
For businesses, the cost savings and efficiency are apparent. But beyond the business side, there’s a broader narrative. Dual sensor drones embody the evolution of technology and its potential to empower industries by presenting a holistic view of the world, bridging the gap between what’s seen and unseen.
Spotlight: Laser Rangefinder in Drones
When it comes to advanced technology in drones, the conversation often orbits around vision capabilities like night vision and thermal imaging. Yet, another tool that’s quietly revolutionizing drone operations is the laser rangefinder.
Laser rangefinders, at their core, are devices that measure the distance between the drone and a specific point on the ground or object. They do this by emitting a laser beam toward the target.
Once the beam hits the target, it reflects back. The device then calculates the time it took for the beam to return, providing a precise distance measurement.
Why is this important for drones? In industries such as construction, agriculture, and surveying, understanding exact distances can be crucial.
For instance, when assessing the height of a building or the depth of a quarry, a laser rangefinder-equipped drone can deliver data with impeccable accuracy. This precision, when combined with the visual data from night vision and thermal imaging, offers a comprehensive picture that’s hard to rival.
The synergy between night vision, thermal imaging, and laser rangefinding creates an impressive triad of capabilities. Night vision offers clarity in low light, thermal imaging spots heat variations, and the laser rangefinder ensures that the data is not only visually comprehensive but also dimensionally precise.
Consider a search and rescue operation in challenging terrain. While night vision can map the landscape and thermal imaging can identify potential survivors by their heat signatures, the laser rangefinder can provide the exact distance to the target, ensuring timely and precise interventions.
In a rapidly evolving drone industry, the integration of these three tools exemplifies how technology can come together to provide solutions greater than the sum of their parts.
For those in the know, it’s clear: drones equipped with night vision, thermal imaging, and laser rangefinding are setting the gold standard for aerial operations.
Best Night Vision Drone on the Market
Navigating the world of drones with night vision capabilities can seem like a daunting task.
Within the expansive range, three standout models from the industry leader, DJI, deserve special attention. Their advancements in night vision technology offer unparalleled utility to users.
Here’s a closer look at their distinctive features and an objective weigh-in on their pros and cons:
DJI Mini 3 Pro
- Features: With its compact design, this model boasts enhanced night vision capabilities. It offers 4K ultra-clear video recording and a commendable 31-minute maximum flight time.
- Pros: Its lightweight nature makes it particularly suitable for beginners. The camera quality is impressive, especially given its relatively affordable price point.
- Cons: It has limited advanced flying features, and the battery life might come up short for extended professional tasks.
DJI Mavic 3 Classic
- Features: This model shines with its dual-camera system, encompassing both telephoto and wide-angle lenses. It promises a 46-minute flight time and excels in night vision performance.
- Pros: Its extended flight duration is a major plus. The advanced camera setup and robust obstacle avoidance system make it ideal for professional-grade tasks.
- Cons: Its premium features come at a higher price, and it might be considered over-the-top for casual or novice users.
DJI Air 2S
- Features: Setting benchmarks with 5.4K video recording, this model has an advanced sensor system that ensures unparalleled clarity during night vision operations. It promises a 31-minute flight time and is equipped with top-tier safety features.
- Pros: The high-resolution camera sets it apart, making it versatile for various user segments. It’s loaded with safety provisions.
- Cons: The battery life, while reasonable, is in line with smaller models. Some users might lean towards a more specialized drone.
The rapidly evolving drone industry sees these three models as game-changers in the realm of night vision operations.
Each model, with its unique strengths and shortcomings, represents the future trajectory of drone tech. For prospective drone owners, these insights can guide a well-informed purchase decision, ensuring the best fit for individual requirements.
Factors to Consider When Buying a Night Vision Drone
When entering the market for a night vision drone, several considerations can sway your decision. Ensuring you pick the right drone tailored to your needs is essential, and this requires a comprehensive understanding of various factors.
Let’s break down the elements you should have on your checklist:
- Purpose and Intended Use Before investing in a drone, identify its primary purpose. Do you need it for professional videography, agricultural surveys, or perhaps, recreational use? Each use case may lean towards different drone specifications, with night vision being particularly useful for surveillance, wildlife monitoring, and nocturnal videography.
- Camera Quality and Resolution The core of any drone’s visual capabilities lies in its camera. Prioritize drones with high-resolution cameras that provide clear images, especially in low-light conditions. For professionals, drones capable of 4K or 5.4K video recording might be non-negotiable.
- Flight Time and Range Longer flight times often translate to more extensive coverage and reduced need for frequent battery swaps. Look for drones that offer a reasonable balance between flight duration and range. Remember, advanced drones can fly further away from their pilot, but ensure you’re always within legal limits and visual sight.
- Budget Considerations While we all want the best specs, it’s crucial to evaluate the cost. Expensive doesn’t always mean better. Determine a budget range and find drones that offer the best value in terms of features and performance within that range.
- Ease of Use for Beginners and Experts Whether you’re a novice or an expert drone pilot, usability can make or break the flying experience. Some drones come with beginner-friendly modes, while others are more suited to seasoned professionals. Ensure the model aligns with your proficiency level.
In essence, the journey to acquiring a night vision drone isn’t just about its nighttime capabilities. It’s about understanding and balancing several factors to match your specific needs.
The Rise of Thermal Drones in Various Industries
The rapid evolution of drone technology has paved the way for specialized tools like thermal camera drones. Their unique ability to detect heat signatures has revolutionized several industries.
With the potential to transform operations and improve efficiency, let’s examine how different sectors are benefiting from the capabilities of these drones.
Agriculture
Farmers have found an invaluable ally in thermal camera drones. By capturing the heat signatures of crops, these drones help in identifying areas that may be under stress due to lack of water or potential diseases. Early detection enables farmers to intervene promptly, leading to healthier crops and potentially higher yields.
Search and Rescue
Time is of the essence in search and rescue operations. With vast terrains and often challenging conditions, locating individuals can be like finding a needle in a haystack. Enter thermal camera drones.
By detecting human heat signatures, rescuers can quickly identify and zero in on lost or injured individuals, significantly improving the chances of a successful rescue.
Surveillance
Monitoring vast areas, especially during the night, is a challenge for security agencies. Thermal drones provide a solution. They can easily detect intruders or unauthorized activities based on heat signatures, making them an indispensable tool in safeguarding sensitive zones or borders.
The marriage of drones with thermal imaging has indeed created a synergy that holds immense potential. From ensuring food security to saving lives, the impact of these drones across industries is profound and undeniable.
Essential Tips for Night Time Drone Operations
Navigating the night sky with a drone is both exhilarating and challenging. The beauty of the nocturnal world is unrivaled, but it also presents a different set of risks and responsibilities for drone operators. Here’s a guide to help ensure your nighttime drone flights are both safe and productive.
- Safety First: Without the clarity of daylight, hazards like power lines, trees, and buildings become even more dangerous. Before launching, scout the area during the day to familiarize yourself with potential obstacles. Equip your drone with obstacle avoidance technology and maintain a clear line of sight.
- Respect Privacy: The quiet of the night amplifies the noise of a drone. Be considerate of residents and wildlife. Avoid flying over private properties or populated areas to minimize disturbances and privacy concerns.
- Adherence to Regulations: Many regions have specific regulations for nighttime drone operations. Stay informed about these and obtain any necessary permits or clearances. Ensure your drone has the required lighting for visibility to other aircraft.
- Maximize Night Vision Benefits: To get the most out of your drone’s night vision capabilities, familiarize yourself with its settings. Understand how to adjust for different lighting conditions and interpret thermal or infrared images.
Preparation and knowledge are paramount for all drone operations. By following these tips, you’ll ensure that your night flights are both enjoyable and safe.
Conclusion
In the evolving world of drone technology, the integration of night vision and thermal imaging is revolutionizing operations across industries.
From understanding the intricacies of these technologies to recognizing their immense value in fields like agriculture and search & rescue, it’s evident that drones with nighttime capabilities are game-changers.
Whether you’re considering purchasing a drone equipped with night vision or simply understanding its applications, it’s vital to be informed and safety-conscious. With the right drone, knowledge, and preparation, the sky—day or night—holds limitless potential.
FAQs
How does night vision technology work in drones?
Night vision in drones primarily uses infrared illumination and thermal imaging, enabling the drone to see in low light conditions and detect heat signatures.
What makes thermal imaging drones different from standard ones?
Thermal imaging drones detect heat signatures and differences in temperature, unlike standard cameras which capture visible light.
Why are dual sensors, combining both night vision and thermal imaging, beneficial in drones?
Drones with dual sensors offer the advantage of seeing in low light conditions and detecting heat, enhancing versatility in various applications.
How is a laser rangefinder useful in drones equipped with night vision?
Laser rangefinders help measure distances and improve accuracy in drone operations, complementing night vision and thermal imaging capabilities.
Which are some of the top night vision drones available in the market?
DJI Mini 3 Pro, DJI Mavic 3 Classic, and DJI Air 2S are among the leading models that offer advanced night vision features.