When navigating through the advanced realms of aerial surveying, the technological duel between photogrammetry and LiDAR sensors becomes a pivotal discussion.
Both, armed with unique capabilities, are the cornerstone of drone technology, pushing the boundaries in capturing high-quality, detailed data across diverse industries, from agriculture to mine inspections.
When it comes to light detection, LiDAR technology crafts detailed 3D point clouds, offering remarkable insights into terrain topography.
Meanwhile, photogrammetry, the art of measuring distances through photographs, stitches together a visual symphony, providing context-rich scans and accessible maps.
Each method, with its distinctive approach to collect data, serves as a linchpin in the evolving landscape of drone surveying, significantly reducing time and resources.
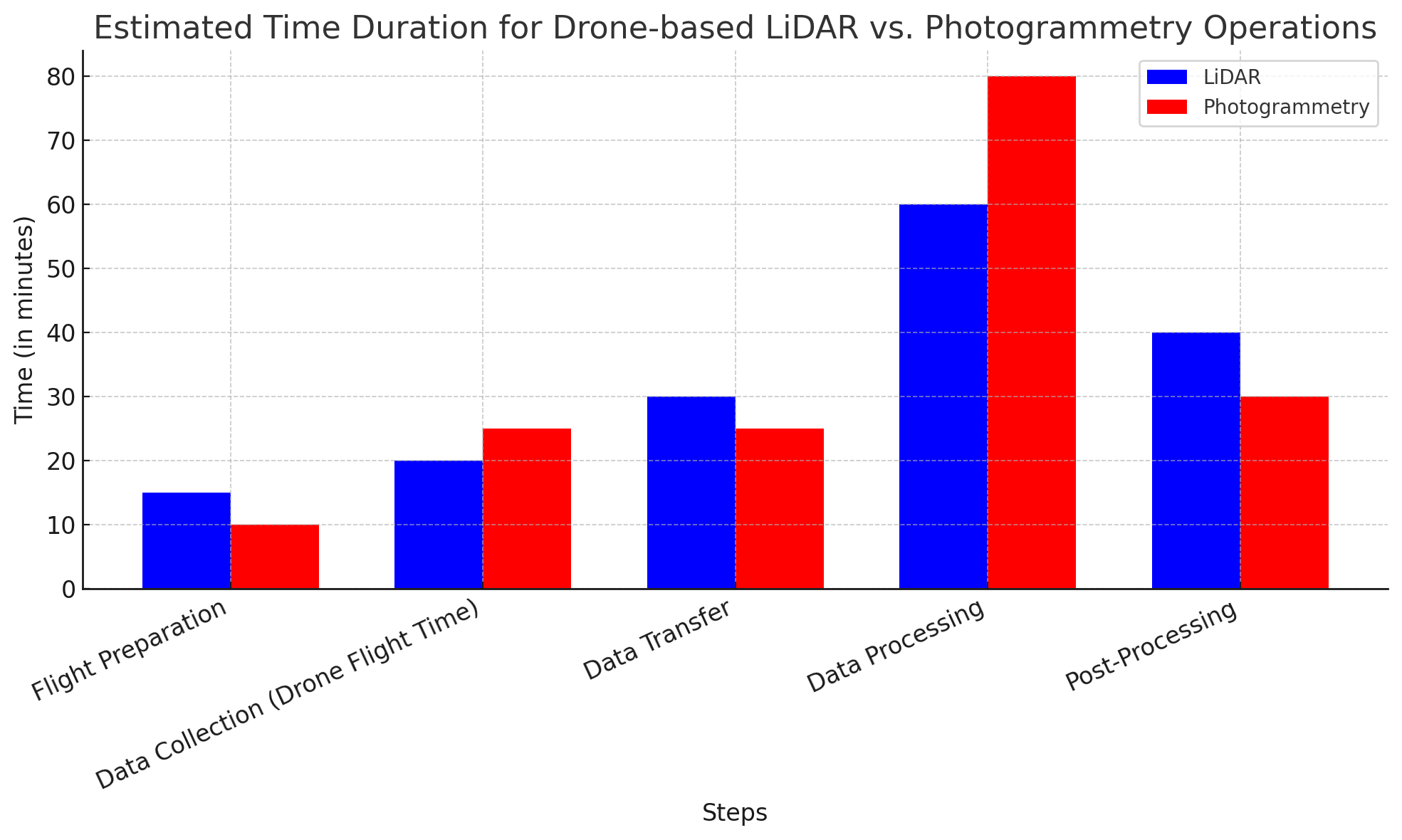
Charts are based on estimates of publicly available data.
Article Highlights:
- Explore the world of drone surveying with a detailed comparison of LiDAR and Photogrammetry, uncovering their unique strengths and practical applications.
- Learn how to balance cost, accessibility, and data quality when choosing between these two cutting-edge technologies for your drone-based projects.
- Discover the essential role of adaptive mission planning software in optimizing data capture efficiency and precision in the realm of LiDAR and Photogrammetry.
Understanding the Basics
Venturing further into the world of drone technology, it’s essential to delve deeper into the mechanisms and intricacies that govern LiDAR and photogrammetry, each offering a distinct perspective of the landscape around us. .
Navigating the realms of LiDAR and photogrammetry in drone surveying requires a nuanced balance between technological prowess and practical considerations.
Definition and Working of LiDAR
Diving deeper into the realm of LiDAR, we find that this technology is more than just a play of light; it’s a symphony of precision, accuracy, and innovation. Every pulsating beam of light tells a story, revealing the hidden contours of the terrain and unmasking the unseen details of our surroundings.
Dylan Gorman created a pretty comprehensive video overviewing how LiDAR is changing the drone surveying industry:
Video Credit: Dylan Gorman
The LiDAR sensor acts as the maestros of this symphony, orchestrating the collection of data points and crafting a comprehensive and detailed representation of the landscape.
The role of the Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) and Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) data in enhancing the functionality of the LiDAR system cannot be understated.
These components are the unsung heroes, ensuring the accurate positioning and orientation of the sensors, and thereby reinforcing the integrity and reliability of the raw data captured.
It’s this harmonious integration that elevates the LiDAR system to a pinnacle of excellence in capturing high-fidelity terrain data.
Definition and Working of Photogrammetry
As we shift our gaze to photogrammetry, we uncover the art and science behind creating realistic and detailed representations of our environment through photographs.
This technique is a testament to the marriage of technology and artistry, where every image captured is a piece of a larger puzzle, meticulously assembled using advanced photogrammetry software to create intricate models and maps.
Source: Bad Decisions Studio
The success of photogrammetry is contingent upon the precision and quality of its tools. The camera’s quality, the attention to image overlap, and the emphasis on Ground Sample Distance (GSD) are the pillars that uphold the accuracy and richness of photogrammetry’s output.
These elements are the building blocks that ensure the creation of detailed and reliable representations of the landscape in drone photogrammetry.
Symbiosis and Integration
Exploring the realms of LiDAR and photogrammetry, it becomes evident that while each technology is formidable on its own, its true potential is realized when they are integrated.
The amalgamation of LiDAR’s precision in capturing elevation data with photogrammetry’s capability to render detailed and textured models results in a comprehensive and multidimensional portrayal of our environment.
The symbiotic relationship between LiDAR and photogrammetry is a testament to the power of collaboration and integration in technology. By combining the strengths of both methodologies, we can achieve a level of detail and accuracy previously thought unattainable, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in drone surveying.
As we navigate through the landscape of drone technology, understanding the basics of LiDAR and photogrammetry is instrumental. These technologies, with their unique mechanisms and applications, serve as the bedrock of modern drone surveying.
By exploring the nuances and intricacies of LiDAR and photogrammetry, we gain invaluable insights into their capabilities and potential, paving the way for innovation and advancement in the field of drone surveying.
The journey of unraveling these technologies is one of discovery and enlightenment, offering a glimpse into the future of drone surveying and the endless possibilities it holds.
Applications of LiDAR and Photogrammetry in Drone Surveying
Navigating through the multifaceted world of drone technology, it becomes evident that the applications of LiDAR and photogrammetry are vast and varied. These technologies serve as the backbone of modern drone surveying, each contributing significantly to the advancements in various fields.
Exploration of Drone LiDAR and LiDAR Remote Sensing Applications
Farming and Landscaping:
In the realm of farming and landscaping, LiDAR is more than just a tool—it’s a game-changer. By meticulously mapping out the topography and assessing vegetation, LiDAR empowers farmers and landscapers to optimize resources and enhance crop yields, fostering sustainability and economic viability.
Terrain Mapping:
LiDAR’s precision in terrain mapping is unparalleled, crafting detailed and accurate representations of Earth’s diverse landscapes. This accuracy is pivotal for urban planning, environmental conservation, and infrastructural development, ensuring harmonious and sustainable interactions between humans and their environments.
Mine Inspections:
Within the complex and hazardous environments of mines, LiDAR is the beacon of safety and efficiency. It navigates through the subterranean networks, assessing structural integrity and ensuring compliance with safety protocols, thereby safeguarding lives and optimizing operations.
Diverse Industries and Environments:
The adaptability of Drone LiDAR technology is showcased in its applications across various sectors, from forestry to urban development. Its ability to capture data in diverse environments with LiDAR Remote Sensing makes it indispensable for research, conservation, and industrial advancements.
Furthering Technological Innovations:
LiDAR is not just confined to the aforementioned applications; its potential is continually being explored and expanded. From aiding autonomous vehicles to contributing to archaeological discoveries, the technology is at the forefront of innovation, shaping the future and solving complex challenges.
Exploration of Photogrammetry Applications
Creation of Orthomosaic Maps and 3D Models:
Photogrammetry stands out in creating intricate orthomosaic maps and detailed 3D models. This visual richness is essential for comprehensive analysis, project planning, and implementation across various fields, such as construction, archaeology, and environmental monitoring.
Visual Assessments and Dataset Analysis:
Photogrammetry excels in providing robust datasets for thorough visual assessments. This capability is invaluable for informed decision-making, ensuring accuracy and reliability in projects ranging from historical preservation to urban development.
Versatile Suitability:
The versatility of photogrammetry is evident in its wide-ranging applications. It adapts to the unique requirements of different industries and projects, proving its efficacy and reliability in diverse scenarios.
Expanding Horizons:
Like LiDAR, photogrammetry continues to evolve and expand its horizons. Its applications in virtual reality, gaming, and film industries showcase its potential to reshape our perceptions and experiences, blending the boundaries between reality and imagination.
Convergence of Applications
As we venture further into the applications of LiDAR and photogrammetry, it’s intriguing to observe their convergence in certain domains. The combination of these technologies enhances data accuracy and comprehensiveness, creating synergies that drive advancements in fields like geospatial analysis, urban planning, and disaster management.
Synergizing for Greater Outcomes:
The amalgamation of LiDAR and photogrammetry results in richer and more detailed datasets, enabling more nuanced analysis and informed decision-making. This synergy is particularly beneficial in large-scale projects and research, where the integration of diverse data points is crucial for success.
Future Prospects:
The exploration of LiDAR and Photogrammetry applications paints a vivid picture of their potential to shape the future. As technology advances, the possibilities are boundless, and the integration of these techniques will continue to unveil new horizons and contribute to the progress of humanity.
In conclusion, the journey through the diverse applications of LiDAR and photogrammetry has been enlightening. These technologies, with their unique attributes and converging potentials, are steering the course of drone surveying and beyond.
They are unlocking new possibilities, solving intricate challenges, and contributing significantly to our understanding of the world and our place in it. The future is ripe with opportunities, and the continued exploration and advancement of these technologies promise a world where the boundaries of what is possible are continually expanding.
Photogrammetry vs LiDAR
Navigating the diverse landscapes sculpted by drone technology, we find ourselves at a crossroads, poised to dissect the comparative elements of LiDAR and photogrammetry.
Both technologies, resplendent in their distinct capabilities, are subject to scrutiny under the lens of accuracy, detail, data capture, and processing.
Here, we shall embark on an enlightening journey, meticulously comparing these methodologies, and unraveling the nuanced distinctions and similarities that characterize them.
Accuracy and Detail
Detail and Accuracy of LiDAR Point Clouds
LiDAR stands as a beacon of precision in the world of drone surveying, crafting highly detailed point clouds that serve as a faithful representation of our environment.
The accuracy of LiDAR point cloud is unparalleled, offering granular insights into the minutiae of the terrain, unearthing the subtle nuances that often remain obscured. The fidelity of the data captured by LiDAR is a testament to the technology’s prowess in revealing the intricate tapestry of our world.
Conditions Influencing the Accuracy of Photogrammetry
Conversely, the accuracy of photogrammetry is inherently influenced by various external conditions. Elements such as lighting, shadow, texture, and camera quality play pivotal roles in determining the fidelity of the resultant models and maps.
Photogrammetry, while versatile, requires a harmonious alignment of conditions to manifest its true potential in detailing the landscapes it seeks to depict.
Comparative Analysis of LiDAR vs Photogrammetry
When placed side by side, LiDAR and photogrammetry present a tableau of contrasts and complementarities. LiDAR, with its unwavering accuracy, excels in scenarios demanding high-detail elevation data, while photogrammetry shines in rendering textured and colored models.
The choice between the two is not a matter of superiority but of appropriateness, dictated by the unique demands and conditions of each surveying scenario.
Data Capture and Processing
Overview of Data Capture Techniques in LiDAR and Photogrammetry
Delving into the realms of data capture, we uncover divergent paths trodden by LiDAR and photogrammetry. LiDAR employs pulsating laser beams, meticulously measuring distances and creating a dense constellation of data points, whereas photogrammetry relies on overlapping photographs, meticulously stitched together to sculpt detailed representations.
These diverse techniques underscore the multifaceted nature of drone surveying, each offering a unique lens through which we perceive our world.
Differences in Processing LiDAR and Photogrammetry Data
The journey from data capture to final representation is characterized by distinct processing pathways for LiDAR and photogrammetry. LiDAR data, rich in elevation information, undergoes a rigorous process of filtering and classification, while photogrammetry data is subject to image alignment, reconstruction, and texturing.
The choice of mapping software plays a critical role, influencing the quality and reliability of the resultant output, thereby shaping our understanding and interpretation of the surveyed landscapes.
As we traverse the fascinating terrains of LiDAR and photogrammetry, the comparative analysis of these technologies reveals a rich tapestry of insights and learnings. The interplay between accuracy, detail, data capture, and processing forms the crux of our exploration, offering a window into the intricate dance of light, shadow, texture, and distance.
In the grand scheme of drone surveying, LiDAR and photogrammetry stand as complementary companions, each bringing a unique perspective and a wealth of possibilities to the table.
Practical Considerations
Navigating the realms of LiDAR and photogrammetry in drone surveying requires a nuanced balance between technological prowess and practical considerations. This exploration is as much about pragmatism as it is about the dance with advanced technology, where factors such as cost, availability, quality, and adaptability play pivotal roles.
LiDAR, renowned for its high accuracy through advanced sensors, often necessitates a significant investment, contrasting with the more economical, camera-based photogrammetry. This balance between cost and precision demands a thorough evaluation of both project requirements and budgetary constraints.
The availability and accessibility of varied software for both technologies further complicate the decision matrix, with considerations extending to user-friendliness, support, and compatibility with different drone platforms.
The art of capturing high-quality data is shaped by meticulous planning and the judicious selection of technology. For LiDAR, aspects like sensor accuracy, environmental conditions, and flight altitude are crucial, while photogrammetry requires a focus on image overlap, camera quality, and lighting.
Adaptive mission planning software, equipped with intelligent features, stands as a beacon of innovation, enabling the optimization of flight paths and ensuring comprehensive data collection, thereby pushing the boundaries of precision and efficiency in drone surveying.
In conclusion, while they may seem mundane, these practical considerations are fundamental to success in utilizing LiDAR and photogrammetry. They guide informed choices and optimized outcomes, illuminating the path to mastery in the dynamic field of drone technology.
Final Thoughts
Navigating through the intricate terrains of LiDAR and photogrammetry has unveiled the pivotal roles these technologies play in the world of drone surveying.
Each, with its unique capabilities and applications, presents a distinctive approach to capturing and interpreting the world from above. We’ve journeyed through the fundamentals, delved into practical considerations, and drawn comparisons to illuminate the path to informed decision-making.
The dance of light with LiDAR and the symphony of images in photogrammetry have showcased the depth of accuracy, detail, and adaptability in various scenarios and industries.
Practical considerations, balancing cost, availability, quality, and adaptability, have emerged as guiding lights, shaping the narrative of choice and application in real-world settings.
In conclusion, the exploration of LiDAR and photogrammetry is a voyage of discovery and insight, propelling us towards mastery in drone surveying.
The knowledge gleaned from this journey equips us with the tools to make informed choices, optimize outcomes, and push the boundaries of what is achievable in the ever-evolving drone landscape.
FAQs
What are the main differences between LiDAR and photogrammetry in drone surveying?
LiDAR uses laser beams to measure distances and create detailed terrain maps, while photogrammetry utilizes photographs to construct models and maps. The choice between the two depends on factors like required accuracy, project specifications, and budget.
How do the costs of using LiDAR and photogrammetry compare?
LiDAR generally requires a higher investment due to its advanced sensors and high accuracy, while photogrammetry, leveraging camera-based technology, is typically a more economical alternative.
What are the practical considerations for capturing high-quality data in drone surveying?
Capturing high-quality data involves considering the technology’s accuracy, environmental conditions, flight altitude for LiDAR, and image overlap, camera quality, and lighting conditions for photogrammetry. Additionally, adaptive mission planning software can optimize data capture.
How does the availability and accessibility of software influence the choice between LiDAR and photogrammetry?
The market offers a variety of software options for both technologies, each with unique features and capabilities. User-friendliness, support, and compatibility with different drone platforms are vital considerations influencing the integration of technology and project objectives.
What roles do LiDAR and photogrammetry play in drone surveying applications?
LiDAR is pivotal in applications like farming, landscaping, terrain mapping, and mine inspections, offering detailed point clouds and accurate terrain depiction. photogrammetry is versatile, suitable for creating orthomosaic maps, 3D models, and visual assessments across various industries and projects.